Cloud River Urban Research Institute

Editor’s note:
Which country is the biggest auto manufacturer? Which country has the biggest auto market? Which Chinese city has the strongest auto industry? Cloud River Urban Research Institute draws on the “radiating strength” of the auto industry in its China Integrated City Index to answer these questions.

The world’s largest auto manufacturer
The auto industry has been hit hard during the pandemic. The global auto production in 2020 slumped to 77.62 million units, down by 15.8% from the 2019 level. In 2021, the global auto production rallied to 80.15 million units, but the figure was only 82.4% of the peak level in 2017.
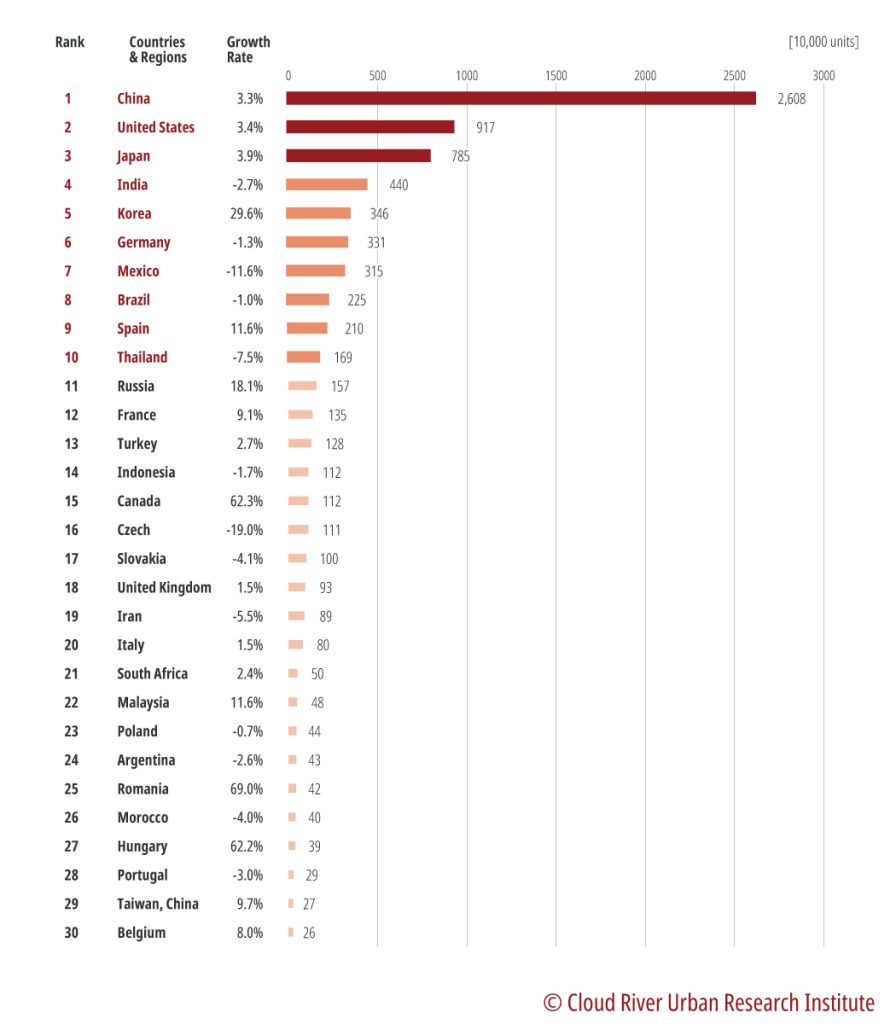
The auto industry represents a country’s comprehensive strength in manufacturing. China has been the world’s largest auto manufacturer. Figure 1 shows that China tops the ranking with a production of 26.08 million units. The figure accounts for 32.5% of the global total, more than tripling that of the U.S., which ranks second. China’s auto output outnumbers that of other top five countries combined – the U.S., Japan, India, and the Republic of Korea.
Figure 1 Top auto manufacturers by country/region in 2021
WTO admission boosts China’s auto industry
The trajectory of auto production from 2000 to 2021 in Figure 2 shows that, China’s auto industry took off in 2001 when the country joined the WTO. Its auto industry leapfrogged the U.S. to become the world’s second largest auto manufacturer in 2008, then replaced Japan as the world’s top auto manufacturer amid the financial crisis in 2009, and has since roared ahead.
Japan replaced the U.S. to become the world’s largest auto manufacturer in 2006, but was dethroned by China in 2009, and then slipped into third place after being surpassed by the U.S. in 2011. Japan has since then been put in the shade with China and the U.S. keeping their widening lead.
Figure 2 Top auto production by major countries from 2000 to 2021

China’s auto exports gain momentum despite the pandemic
The pandemic dealt a heavy blow to the global supply chain and the auto export alike. Figure 3 shows that the world’s top 30 auto exporters, excluding China and Slovakia, saw decreases in auto exports in 2020, some even registering a double-digit decline. In 2020, China bucked the trend to achieve a 3.4% growth rate, while the global exports slipped by 14.7%.
China, however, came in fifth in the ranking of auto exports despite the sheer size of its auto manufacturing. Professor Zhou Muzhi, head of Cloud River Urban Research Institute projected that while automobiles produced in China are largely consumed by the domestic market with low export rates, the world’s largest auto manufacturer is set to become the world’s largest auto exporter buoyed by a large market.
Figure 3 Top auto exports by country/region in 2020


Two juggernauts of the world’s auto industry
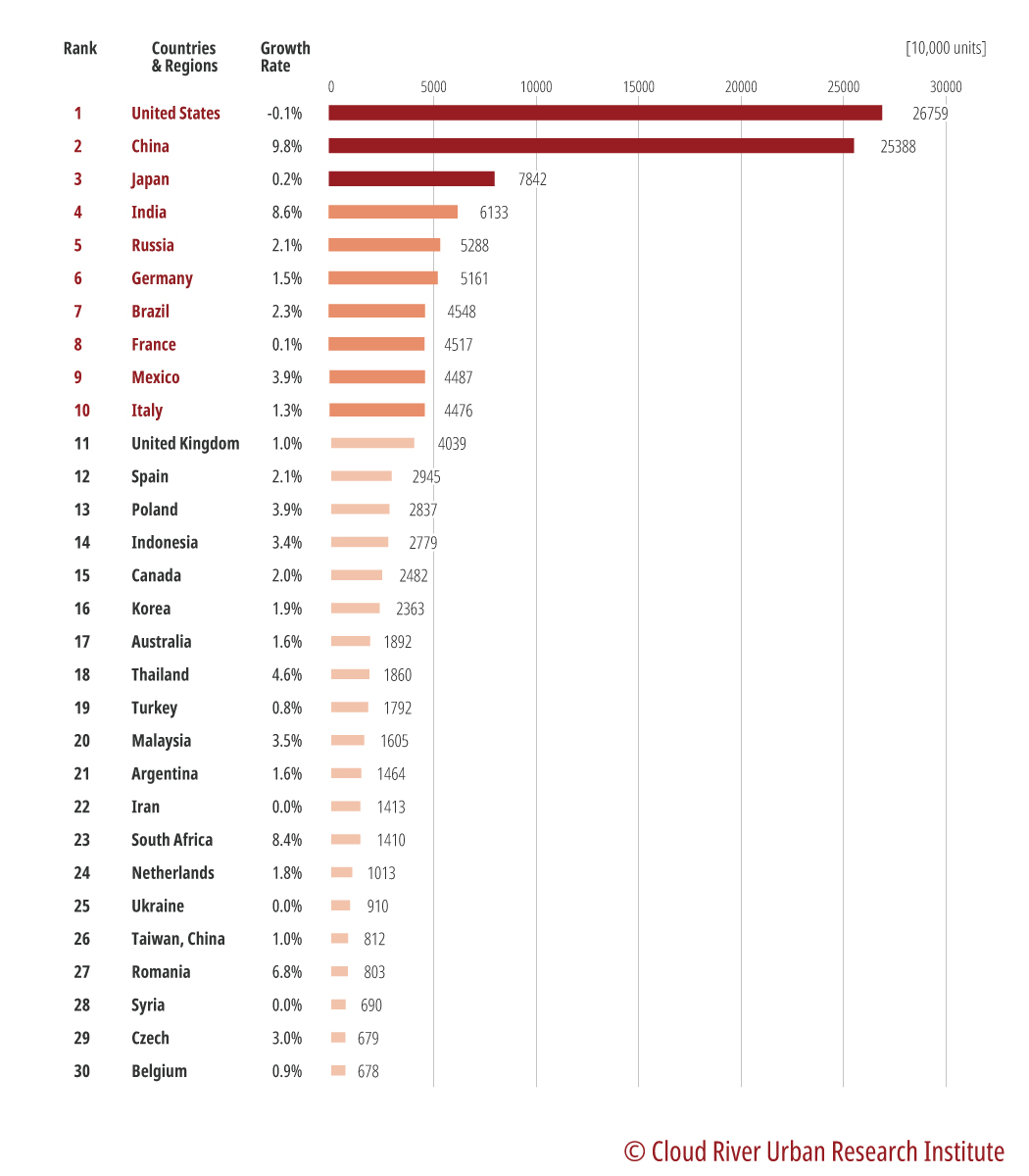
The ranking of car ownership worldwide in Figure 4 provides basis for Zhou’s projection. The top two countries in the ranking – the U.S. and China – leave Japan in third place way behind, with a combined 35% of the world’s car ownership. The figure is even higher than the combined car ownership of countries in places from third to 12th. It is fair to say that China and the U.S. are two juggernauts of the world’s auto industry.
Figure 4 Top car ownerships by country/region in 2019
Which country has the most open and diversified auto market?
In Figure 5, the U.S., reigning in the ranking, accounted for 20% of the world’s total auto exports in 2020, more than doubling the figure of Germany, which takes second place in the ranking.
Despite ranking second in terms of auto production, the U.S. has to import a large number of automobiles from Germany and Japan. Germany is the world’s largest auto exporter and the world’s second largest auto importer. Different from the U.S. and Germany, Japan’s auto imports only rank 15th in the world. Due to its reluctance to import yet strong exports, the auto industry remains Japan’s largest export sector.
Despite ranking third in terms of auto imports, China has exported more vehicles than imported vehicles, emerging as a net exporter.
Figure 5 Top auto imports by country/region in 2020
Auto industry becomes pillar of Chinese economy
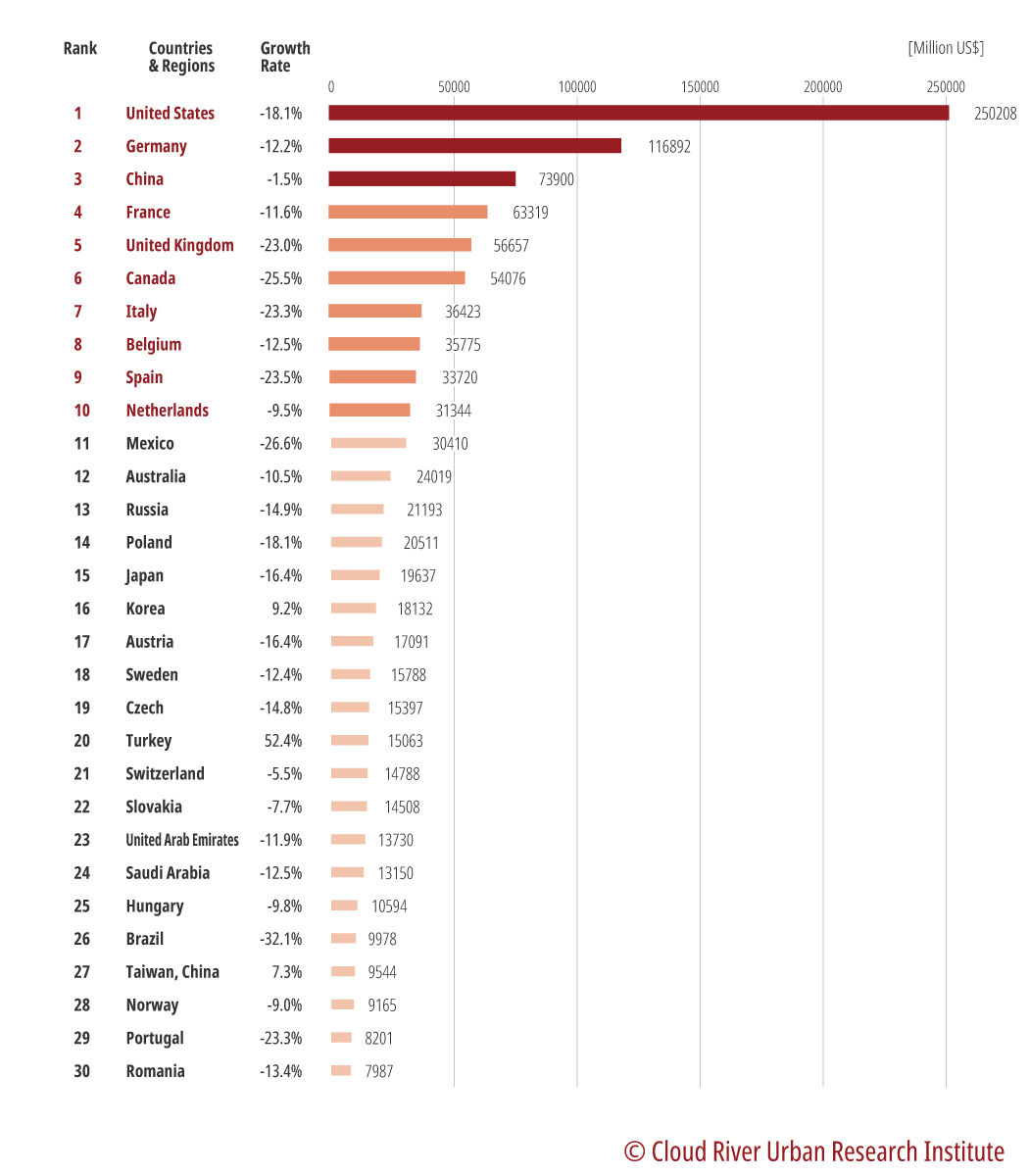
The auto industry is a pillar that props up China’s economic growth. Figure 6 shows China tops the ranking of the value added of the auto industry. China occupies 28.1% of the global value added of the auto industry in 2019, twice that of the U.S. in second place.
The high added value present in the market will pit automakers worldwide against each other. The auto industry has rapidly grown into a pillar of China’s economy.
Figure 6 Ranking of the value added of the auto industry by country/region in 2019

Which city has the strongest auto industry?
China Integrated City Index observes 297 Chinese cities at prefecture level and above based on their “radiating strength” in the auto industry. Radiating strength is an index used to assess the influence of a certain industry of a city. Auto radiating strength is an index based on the auto industry’s payrolls, enterprise concentration, and enterprise capital. “The radiating strength of the auto industry of Chinese cities” also looks to data from the Fourth National Economic Census issued by Chinese cities between 2019 and 2020.
The top 10 cities in the ranking of “the radiating strength of the auto industry of Chinese cities” in 2020 are Shanghai, Changchun, Chongqing, Guangzhou, Wuhan, Suzhou, Beijing, Shiyan, Tianjin, and Xiangyang. Among them, the top three cities gain a dominant lead over other cities.
Shenyang, Liuzhou, Wuxi, Chengdu, Nanjing, Wuhu, Ningbo, Nanchang, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Changsha, Shenzhen, Jinan, Wenzhou, Xi’an, Qingdao, Foshan, Hefei, and Zhengjiang take places from 11th and 30th. Zhou concluded that headquarters and flagship factories of vehicles and auto parts mostly cluster in the top 30 cities.
Figure 7 Top Chinese cities in terms of radiating strength in the auto industry in 2020

China’s auto industry took off in 1953 when its first auto factory was established in northeastern China’s Changchun by dint of technologies provided by the Soviet Union. Since reform and opening up in 1978, many foreign auto makers have set up manufacturing bases in China. Chinese automakers have grown rapidly due to their cooperation and competition with their foreign counterparts, turning China into the world’s largest auto manufacturer.
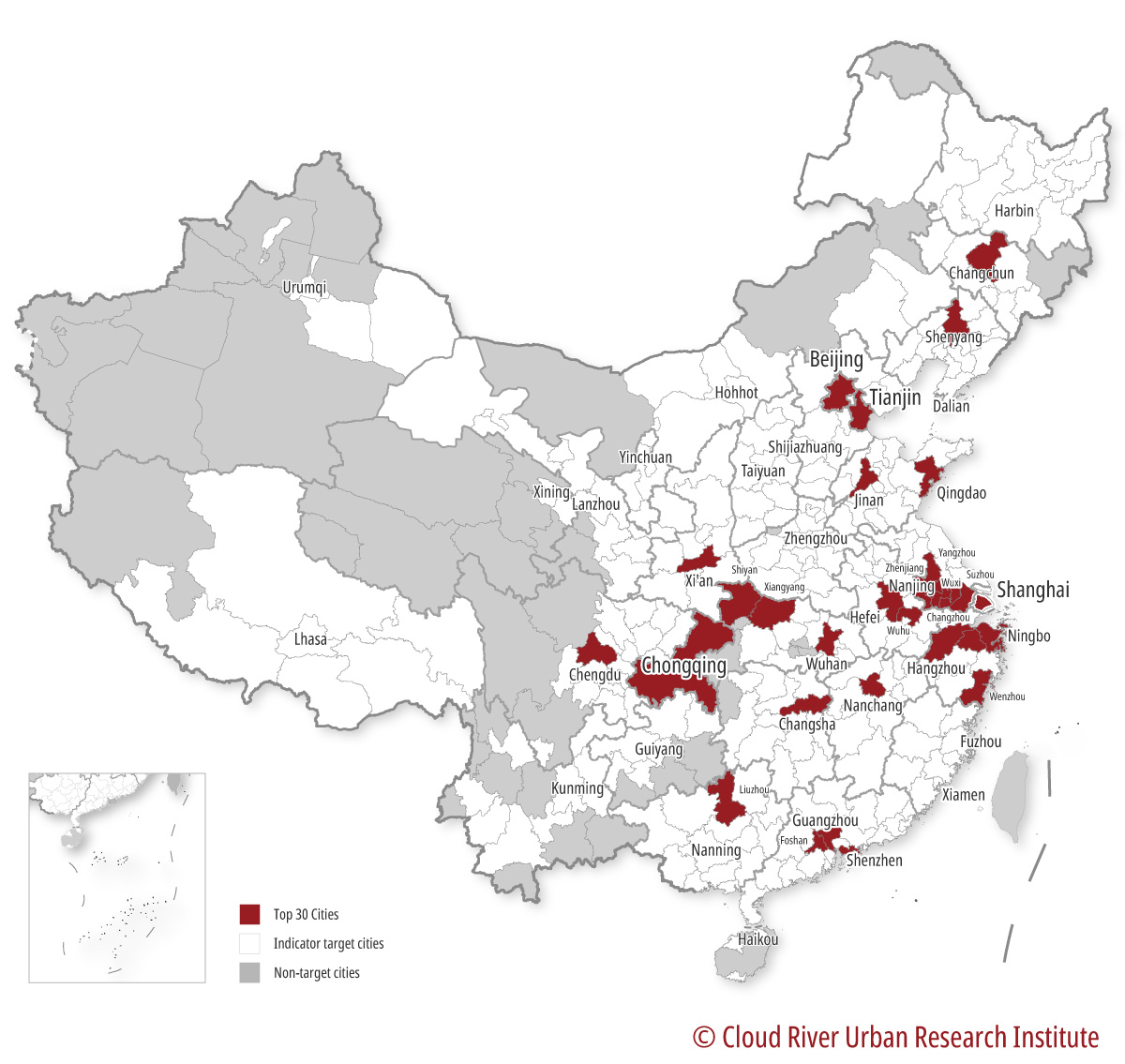
As shown in Figure 8, the top 30 cities in the ranking spread across the country, with Shanghai in the east, Chongqing and Chengdu in the west, Changchun in the north, and Shenzhen in the south. Zhou said, such a distribution is a result of China’s auto industry policies since the founding of the PRC, as these cities home to auto makers cover industrial bases in China’s northeastern, southwestern, northwestern and coastal areas.
Figure 8 Map of top 30 Chinese cities in terms of strength in the auto industry in 2020
Industrial concentration
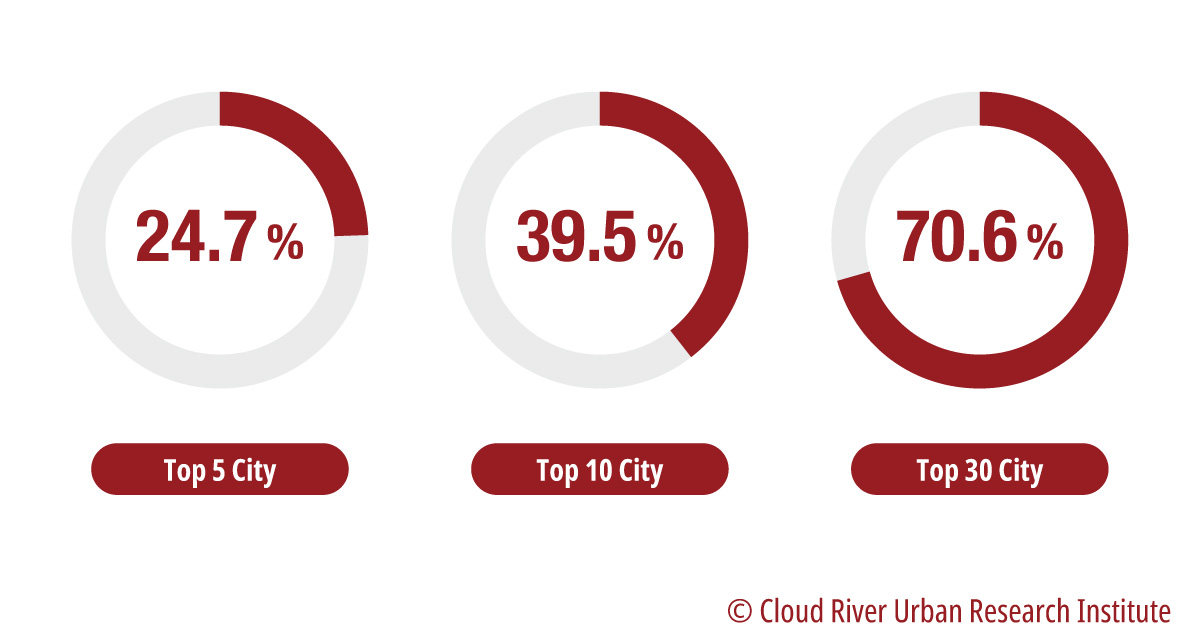
As shown in Figure 9, the top five cities in the ranking – Shanghai, Changchun, Chongqing, Guangzhou, and Wuhan – account for almost one fourth of the payrolls in the auto industry in the country. The proportion is 39.5% and a whopping 70.6%, when the top 10 cities and the top 30 cities are put in the perspective, respectively. That shows the auto industry clusters in these cities.
Figure 9 Concentration of payrolls in the Chinese auto industry in 2020
In terms of sales, Figure 10 shows that the top cities in the ranking account for 36.3% of the national auto sales. The proportion is a staggering 51.3% and 81.1%, when the top 10 cities and the top 30 cities are put in the perspective, respectively.
Zhou said these proportions reflect that China’s auto industry highly concentrates in these cities that can deliver more profits in the auto industry than other cities.
Figure 10 Concentration of sales in the Chinese auto industry in 2020

Revolution of EVs
Electronic vehicles (EVs) have reshaped the global market and came as a boon to China’s auto industry.
In 2021, the global EV sales reached 6.5 million units, up 108% year on year. China took the first spot with 2.94 million units, accounting for 45% of the global sales.
Tesla was the world’s largest EV manufacturer in 2021, followed by BYD and SAIC Motor. The top 20 auto makers contributed a combined 47.63 million units in sales, accounting for 73.3% of the global sales. Eight Chinese EV manufacturers made the top 20 list. As Tesla has a gigafactory in Shanghai, about 40% of the world’s EVs were produced in China. Japan only had one automaker among the top 20, despite the fact that Japan is a large auto manufacturer. In 2021, China exported 500,000 EVs, tripling its 2020 level. The strong showing catapulted China into the top of the echelon as the world’s largest EV exporter, followed by Germany and the U.S.
Data from U.S. consultancy Companys Market Cap revealed that driven by its strength in EV production, BYD overtook Volkswagen to become the world’s third most valuable automaker in June 2022, behind Tesla and Toyota.
Zhou predicted that Chinese-made EVs will dominate the global market in the near future.
The article was first published on China SCIO, China.org.cn on Aug. 15, 2022 and reprinted by other news websites.
